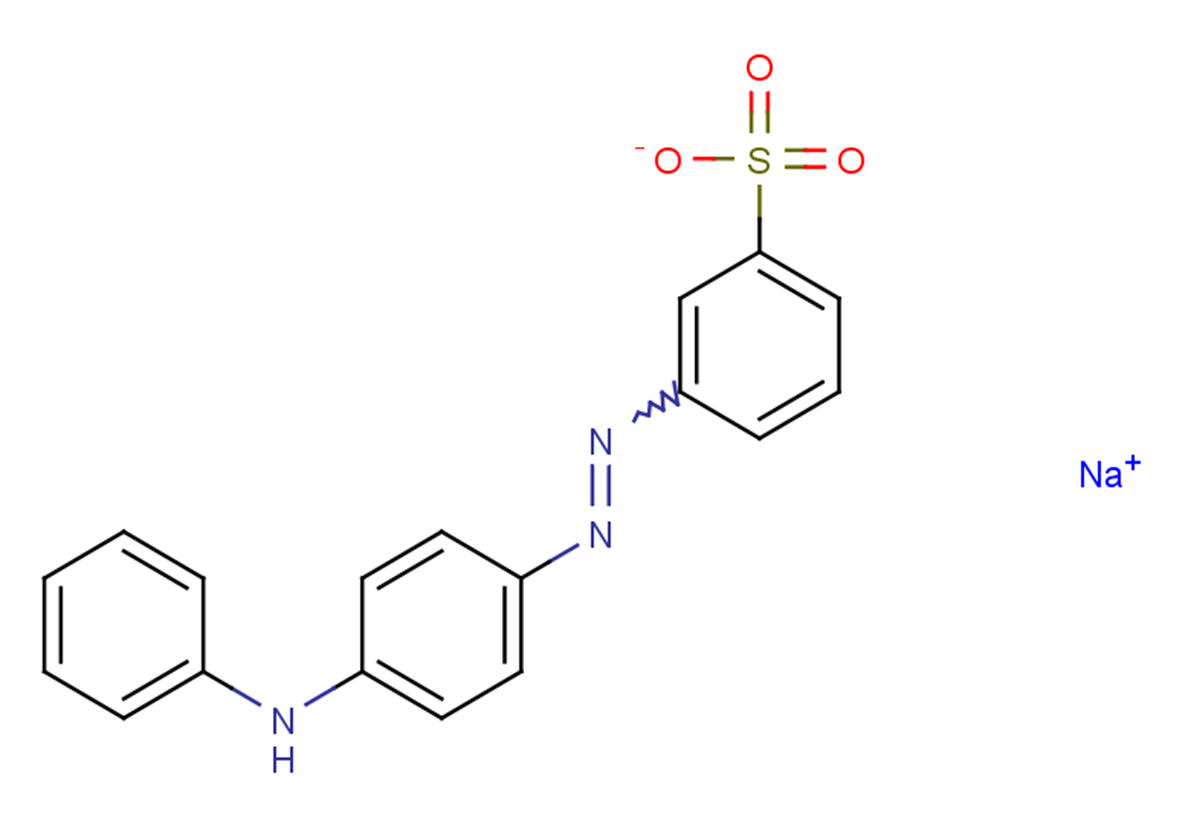
Acid Yellow 36
CAS No. 587-98-4
Acid Yellow 36( Metanil Yellow )
Catalog No. M24579 CAS No. 587-98-4
Acid Yellow 36 is an azo dye and a pH indicator. Acid Yellow 36 changes its color from red at pH 1.2 to yellow at pH 2.3.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 31 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 146 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 219 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 417 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAcid Yellow 36
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAcid Yellow 36 is an azo dye and a pH indicator. Acid Yellow 36 changes its color from red at pH 1.2 to yellow at pH 2.3.
-
DescriptionAcid Yellow 36 is an azo dye and a pH indicator. Acid Yellow 36 changes its color from red at pH 1.2 to yellow at pH 2.3.
-
In VitroAcid Yellow 36(Metanil Yellow) acts as an inducer of a specific form of microsomal P-450 and cytosolic glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and quinone reductase (QR), which may involve a cytosolic Ah receptor.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsMetanil Yellow
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number587-98-4
-
Formula Weight375.38
-
Molecular FormulaC18H14N3NaO3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:24 mg/mL?(63.93 mM;?Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESO=S(C1=CC=CC(N=NC2=CC=C(NC3=CC=CC=C3)C=C2)=C1)([O-])=O.[Na+]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sharma UK, et al. Ameliorating efficacy of eugenol against metanil yellow induced toxicity in albino Wistar rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;126:34-40.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ethaselen
Ethaselen (BBSKE) is an orally active and selective thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR) inhibitor with anticancer activity that directly inhibits TrxR1 activity and is commonly used in combination with oxaliplatin to inhibit tumor growth.
-
Prenyletin
Prenyletin is a natural product found in the multilobed bimodal, multihorned pterosaurs.
-
Epirizole
Epirizole is a pyrimidinyl pyrazole with antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


